BIG SCIENCE IN A SMALL PACKAGE
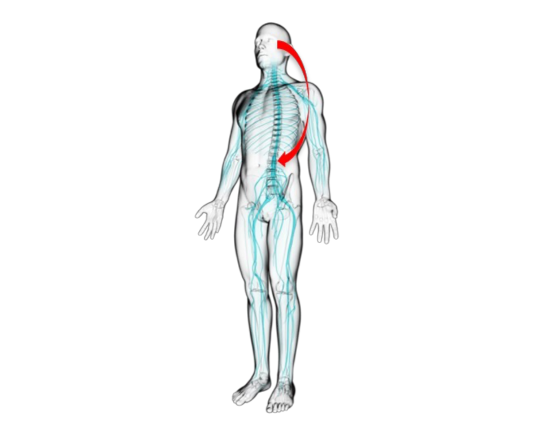
our science changed the game
Invented by a nobel-prize winning neuroscientist, HOTSHOT is proven to work by researchers at Penn State University and in field studies.
Results have shown:
- HOTSHOT significantly reduces muscle-cramp intensity and duration
- Prevents muscle cramps when taken before, during or after a workout
- Research also proved muscle soreness reduction in more than 90% of athletes in a 2 week study
Results presented at:
- American Academy of Neurology
- Society for Neuroscience
- Muscle & Nerve Magazine
- American Medical Athletic Association Journal.
Interested in our science? Email us for more information.
shop now
-
HOTSHOT 6 pack
4.772727272 / 5.0
(220) 220 total reviews
Regular price $29.95 USDRegular price -
HOTSHOT for Muscle Cramps
24 Pack4.772727272 / 5.0
(220) 220 total reviews
Regular price $95.00 USDRegular price -
HOTSHOT For Muscle Cramps
12 Pack4.772727272 / 5.0
(220) 220 total reviews
Regular price $51.50 USDRegular price -
HOTSHOT For Muscle Cramps
12 Pack Subscription5.0 / 5.0
(7) 7 total reviews
Regular price $40.80 USDRegular price
"I took HOTSHOT before the start and at the halfway point. No cramps for the second year in a row taking it."
William DiTullio
Marathoner

"I used it for the first time at a local half marathon 2 weeks ago…I took a HOTSHOT 15 min before (as directed), and never cramped once. Finished 4th at 1:28, pain free and sold on this product!"
Anja Petterson
Ultra Runner, Sports LMP, and UESCA Certified Running Coach

"I took a HOTSHOT before the competition and one just after the hardest of the 6 workouts - I felt pain-free and as things went on, I was more and more mentally comfortable knowing HOTSHOT was working to keep my body feeling good."
Eric Fireman
CrossFit Competitor

"HOTSHOT is one step ahead by attacking the problem at its most direct source: the nervous system.”
Dr. Thomas Ball
Triathlete and Chiropractic Physician

"We strongly encourage athletes to carry HOTSHOT with them as a safety net out on the course.”
Lars Finanger
Swimrun Event Director, Triathlete & Managing Director at Valhalla Sports Group




